| PhotovoltaicWhat is Solar Energy? The term solar energy or solar power describes the methods used to produce energy from sunlight. Solar energy can be used either as a heat source or as an electrical power source. The process of converting the sun's rays into electricity is photovoltaic (PV).
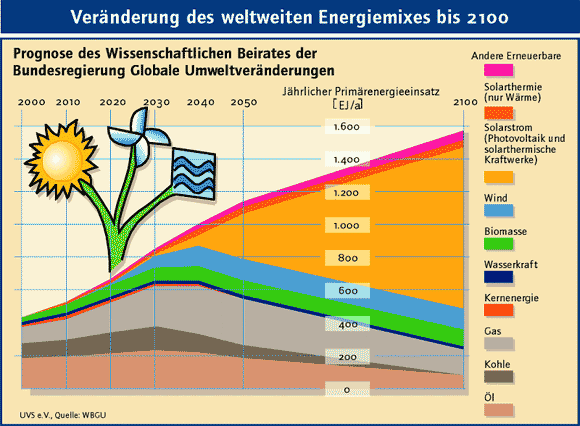
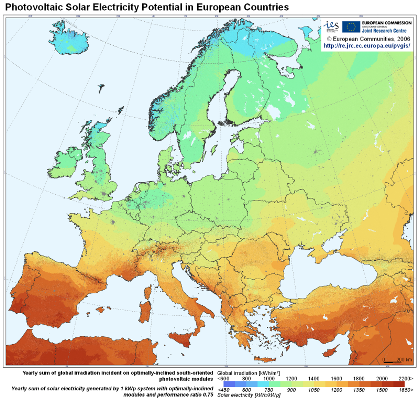
In many parts of the world PV is cost competitive with fossil fuels and other energy solutions. While the world´s fossil fuel is becoming scarce and has a negative impact on the environment. More and more people are deciding to use solar photovoltaic as an energy source. The broad recognition of solar energy in Japan, Germany, Spain, Italy and Greece will result in the solar photovoltaic energy playing an increasingly important role in the world.
What is Photovoltaic?
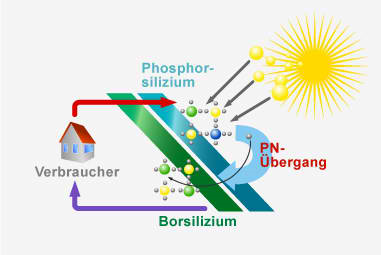
Photovoltaic (PV) is a term that describes the conversion of sunlight into electricity with no moving parts, noise, pollution or fuel. You may have seen calculators or traffic displays powered by solar cells. The term "photovoltaic" comes from the Greek jwV (phos) meaning "light", and "voltaic", meaning electric, from the name of the Italian physicist Volta, after whom a unit of electromotive force, the volt, is named. How does a photovoltaic cell work
The solar cell
More than 90% of today's solar cells are produced from manufactured silicon, a semiconductor. Silicon is is made from sand so there is an almost unlimited supply. Sunlight is composed of small bundles of energy (photons), which act like little bullets. When photons strike a PV cell, they may be reflected, pass through or be absorbed. Only the absorbed photons provide energy to generate electricity.
The solar cell works in three steps:
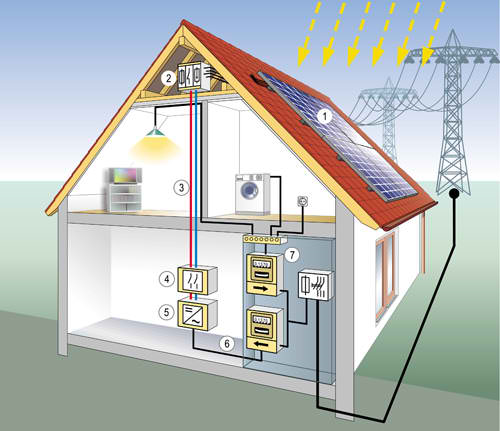
A certain number of modules are connected to fields or systems that emit a certain current performance to suit the application or the demand.
The sun shining on the PV solar cell or system generates direct current and can be used to power various applications. PV can be used for many applications from the power grid to the single-grid supply in remote locations. (In remote houses, the PV is often the only way to produce, electricity). The business with the sun begins right here.
We have to transform the direct current that we produce in our PV system (1), via a so-called inverter (5) into an alternating current. Now the electricity is ready to be fed into the Greek electricity system. Previously we signed a contract with the DEH, (Greek electricity company), in which the DEH agree to buy all electricity that we produce, for 20 years, every minute the sun is shining. Since Greece has a lot of sunshine, we can produce much more electricity than in Germany. By the way, the payment per kWh (kilowatt hours) in Greece is currently almost the highest in the world (as of Oct. 2010).
|  |